Mouth cancer refers to cancer that develops in any of the parts that make up the mouth (oral cavity). Mouth cancer can occur on the:
- Lips
- Gums
- Tongue
- Inner lining of the cheeks
- Roof of the mouth
- Floor of the mouth (under the tongue)
Cancer that occurs on the inside of the mouth is sometimes called oral cancer or oral cavity cancer.
Mouth cancer is one of several types of cancers grouped in a category called head and neck cancers. Mouth cancer and other head and neck cancers are often treated similarly.
Causes
Tobacco and alcohol use. Tobacco use of any kind, including cigarette smoking, puts you at risk for developing oral cancers. Heavy alcohol use also increases the risk. Using both tobacco and alcohol increases the risk even further.
HPV. Infection with the sexually transmitted human papillomavirus (specifically the HPV 16 type) has been linked to oral cancers.
Age. Risk increases with age. Oral cancers most often occur in people over the age of 40.
Sun Exposure. Cancer of the lip can be caused by sun exposure.
Symptoms
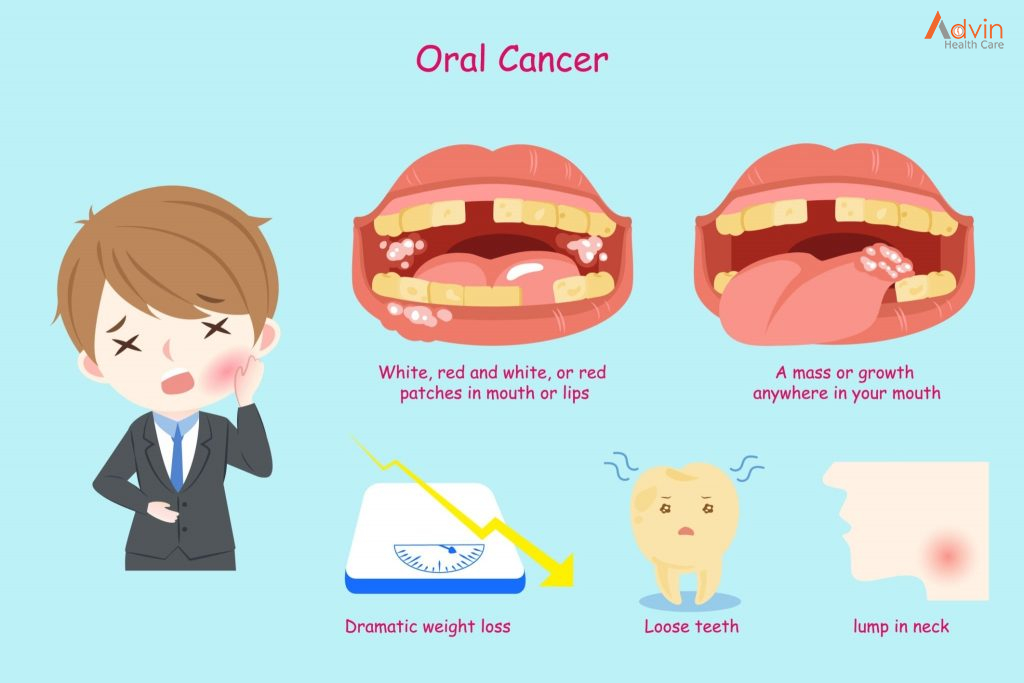
If you have any of these symptoms for more than two weeks, see a dentist or a doctor.
- A sore, irritation, lump or thick patch in your mouth, lip, or throat.
- A white or red patch in your mouth.
- A sore throat or a feeling that something is caught in your throat.
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking.
- Difficulty moving your jaw or tongue.
- Swelling of your jaw that causes dentures to fit poorly or become uncomfortable.
- Numbness in your tongue or other areas of your mouth.
- Ear pain.
Diagnosis
Tests and procedures used to diagnose mouth cancer include:
Physical exam. Your doctor or dentist will examine your lips and mouth to look for abnormalities — areas of irritation, such as sores and white patches (leukoplakia).
Removal of tissue for testing (biopsy). If a suspicious area is found, your doctor or dentist may remove a sample of cells for laboratory testing in a procedure called a biopsy. The doctor might use a cutting tool to cut away a sample of tissue or use a needle to remove a sample. In the laboratory, the cells are analyzed for cancer or precancerous changes that indicate a risk of future cancer. Determining the extent of the cancer
Once mouth cancer is diagnosed, your doctor works to determine the extent (stage) of your cancer. Mouth cancer staging tests may include:
Using a small camera to inspect your throat. During a procedure called endoscopy, your doctor may pass a small, flexible camera equipped with a light down your throat to look for signs that cancer has spread beyond your mouth.
Imaging tests. A variety of imaging tests may help determine whether cancer has spread beyond your mouth. Imaging tests may include X-ray, CT, MRI and positron emission tomography (PET) scans, among others. Not everyone needs each test. Your doctor will determine which tests are appropriate based on your condition.
Mouth cancer stages are indicated using Roman numerals I through IV. A lower stage, such as stage I, indicates a smaller cancer confined to one area. A higher stage, such as stage IV, indicates a larger cancer, or that cancer has spread to other areas of the head or neck or to other areas of the body. Your cancer’s stage helps your doctor determine your treatment options.
Treatment
Treatment for mouth cancer depends on your cancer’s location and stage, as well as your overall health and personal preferences. You may have just one type of treatment, or you may undergo a combination of cancer treatments. Treatment options include surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Discuss your options with your doctor.
Surgery
Surgery for mouth cancer may include:
- Surgery to remove the tumor.Your surgeon may cut away the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue that surrounds it to ensure all of the cancer cells have been removed. Smaller cancers may be removed through minor surgery. Larger tumors may require more-extensive procedures. For instance, removing a larger tumor may involve removing a section of your jawbone or a portion of your tongue.
- Surgery to remove cancer that has spread to the neck.If cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes in your neck or if there’s a high risk that this has happened based on the size or depth of your cancer, your surgeon may recommend a procedure to remove lymph nodes and related tissue in your neck (neck dissection). Neck dissection removes any cancer cells that may have spread to your lymph nodes. It’s also useful for determining whether you will need additional treatment after surgery.
- Surgery to reconstruct the mouth.After an operation to remove your cancer, your surgeon may recommend reconstructive surgery to rebuild your mouth to help you regain the ability to talk and eat. Your surgeon may transplant grafts of skin, muscle or bone from other parts of your body to reconstruct your mouth. Dental implants also may be used to replace your natural teeth.
Surgery carries a risk of bleeding and infection. Surgery for mouth cancer often affects your appearance, as well as your ability to speak, eat and swallow.
You may need a tube to help you eat, drink and take medicine. For short-term use, the tube may be inserted through your nose and into your stomach. Longer term, a tube may be inserted through your skin and into your stomach.
Your doctor may refer you to specialists who can help you cope with these changes.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is most often delivered from a machine outside of your body (external beam radiation), though it can also come from radioactive seeds and wires placed near your cancer (brachytherapy).
Radiation therapy is often used after surgery. But sometimes it might be used alone if you have an early-stage mouth cancer. In other situations, radiation therapy may be combined with chemotherapy. This combination increases the effectiveness of radiation therapy, but it also increases the side effects you may experience. In cases of advanced mouth cancer, radiation therapy may help relieve signs and symptoms caused by the cancer, such as pain.
The side effects of radiation therapy to your mouth may include dry mouth, tooth decay and damage to your jawbone.
Your doctor will recommend that you visit a dentist before beginning radiation therapy to be sure your teeth are as healthy as possible. Any unhealthy teeth may need treatment or removal. A dentist can also help you understand how best to care for your teeth during and after radiation therapy to reduce your risk of complications.
Chemotherapy
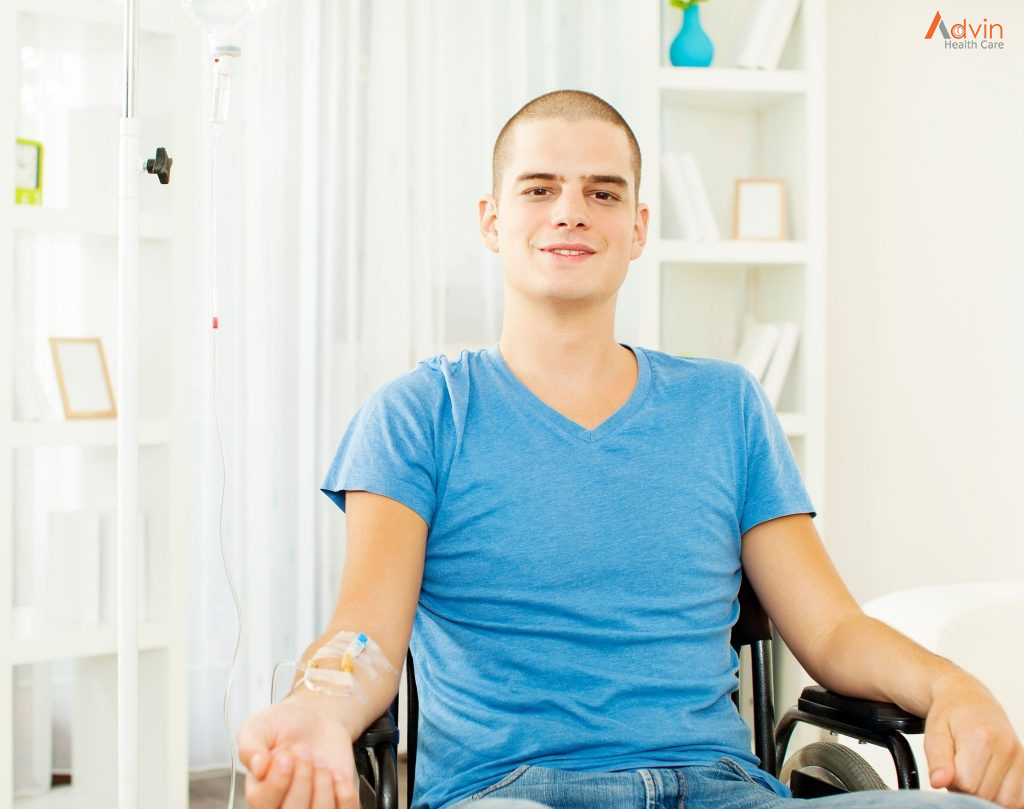

Chemotherapy is a treatment that uses chemicals to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs can be given alone, in combination with other chemotherapy drugs or in combination with other cancer treatments. Chemotherapy may increase the effectiveness of radiation therapy, so the two are often combined.
The side effects of chemotherapy depend on which drugs you receive. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting and hair loss. Ask your doctor which side effects are likely for the chemotherapy drugs you’ll receive.
Targeted drug therapy
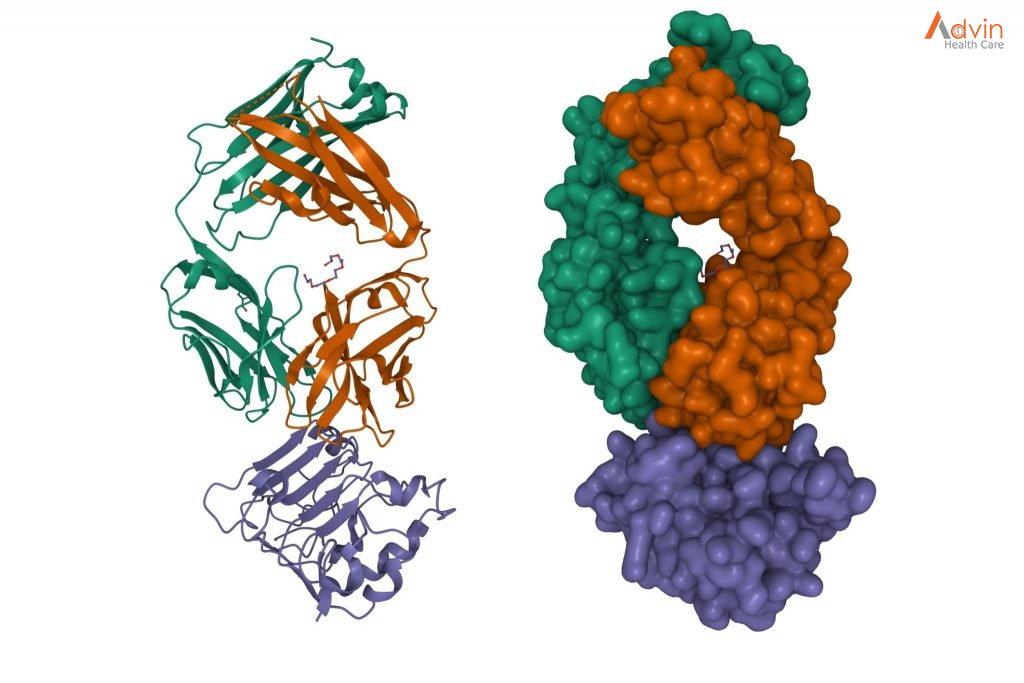
Targeted drugs treat mouth cancer by altering specific aspects of cancer cells that fuel their growth. Targeted drugs can be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Cetuximab (Erbitux) is one targeted therapy used to treat mouth cancer in certain situations. Cetuximab stops the action of a protein that’s found in many types of healthy cells, but is more prevalent in certain types of cancer cells. Side effects include skin rash, itching, headache, diarrhea and infections.
Other targeted drugs might be an option if standard treatments aren’t working.
Immunotherapy
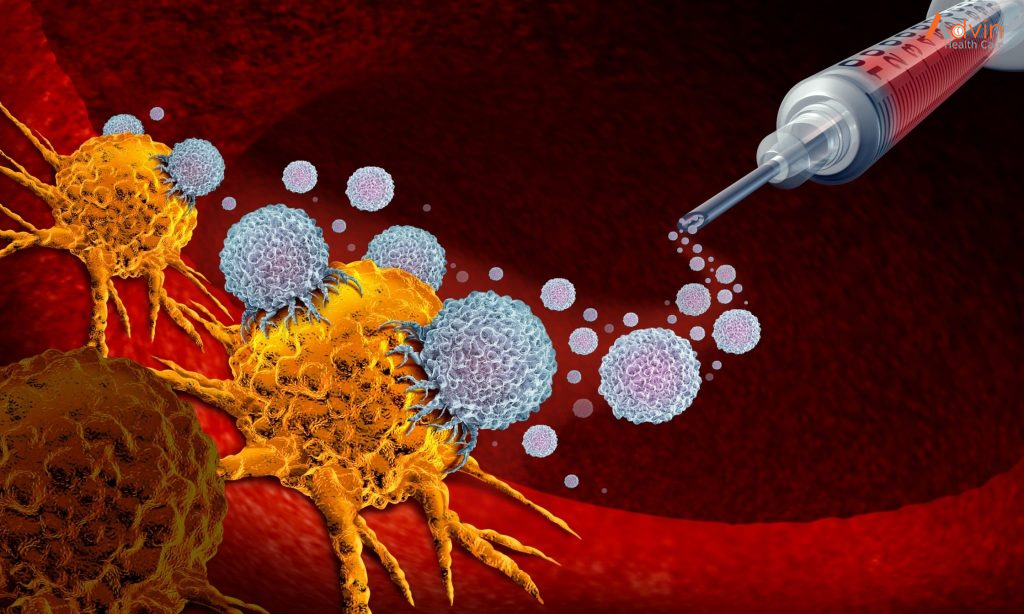
Immunotherapy uses your immune system to fight cancer. Your body’s disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process.
Immunotherapy treatments are generally reserved for people with advanced mouth cancer that’s not responding to standard treatments.