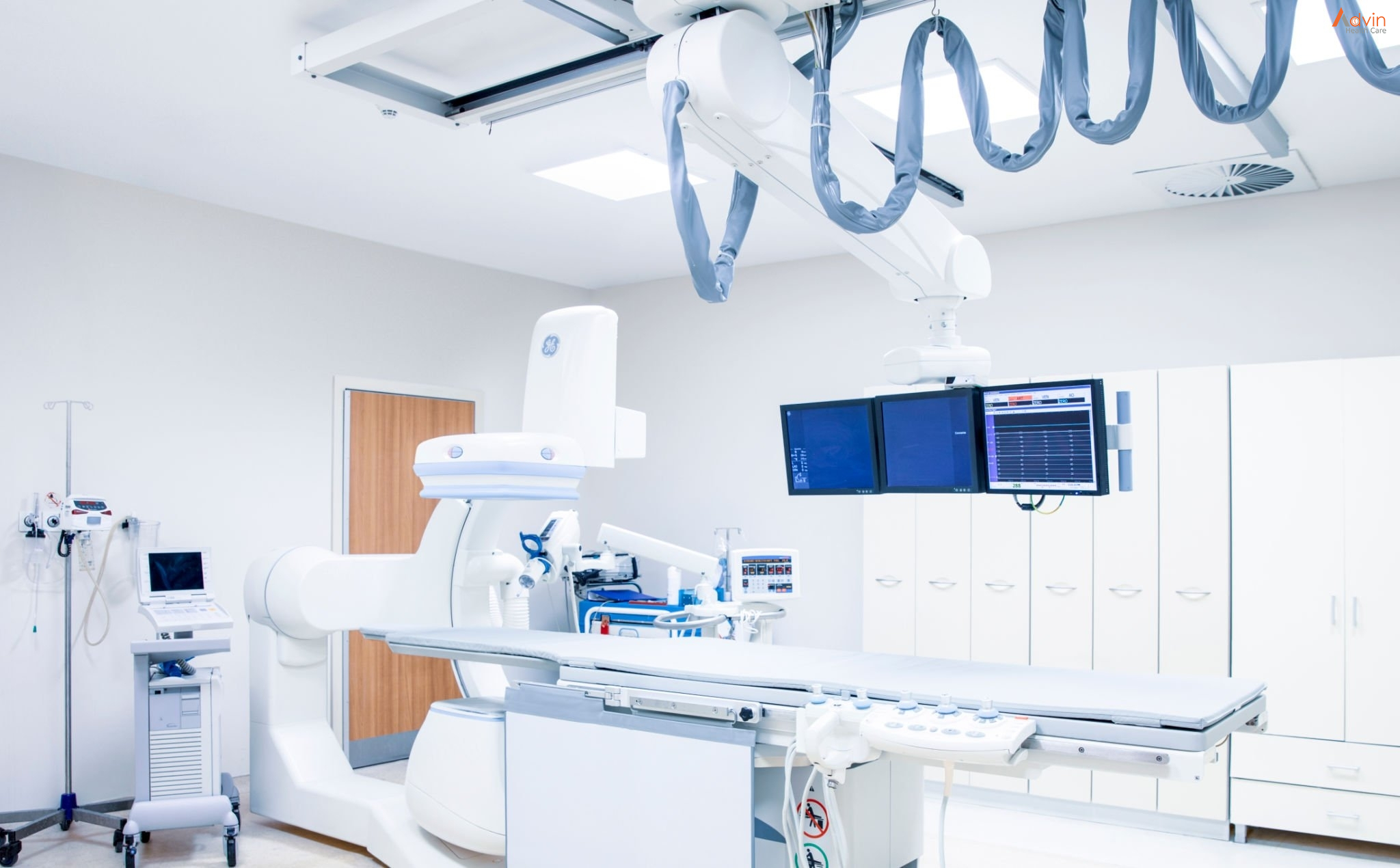
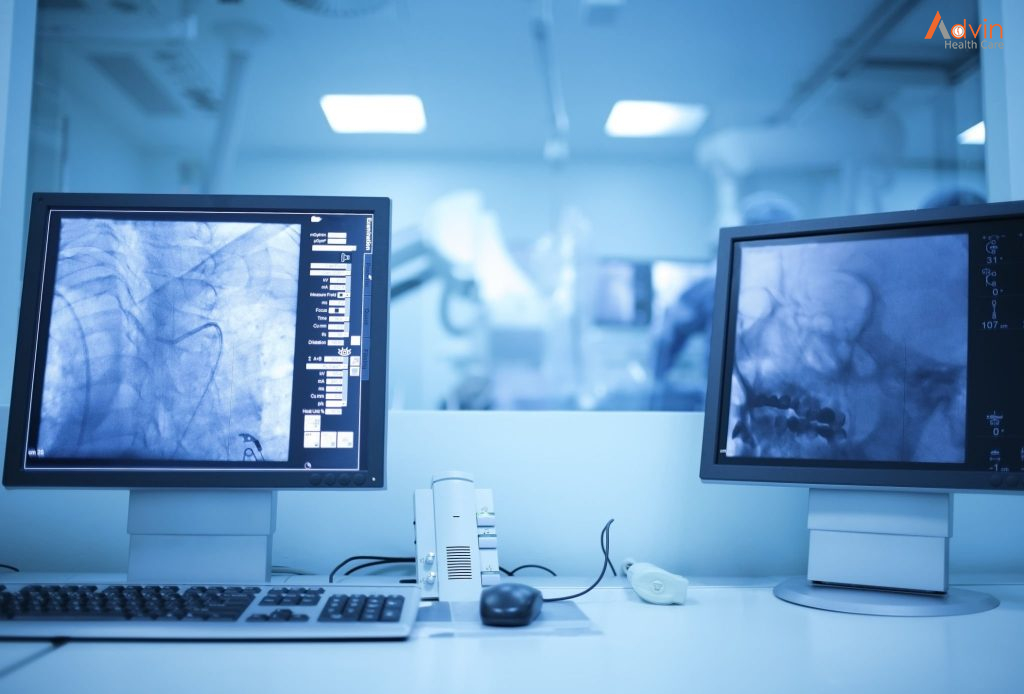
What is a Cath Lab?
The name cath lab sounds a little like something out of a science fiction movie. And in fact, the way that medical professionals use these spaces is a bit futuristic. Cath labs are used to treat patients with heart conditions minimally, without resorting to major surgeries or other invasive procedures. Your healthcare provider may recommend a test or treatment in the cath lab if they need to better understand the state of your heart.
Cath labs are an important part of treating heart conditions. A catheterization laboratory, or cath lab, is a procedural hospital room where minimally invasive tests and procedures are performed to diagnose and treat cardiovascular disease. The procedures performed in a cath lab involve tiny, flexible tubes called catheters which is where the name is derived from. These catheters can be used as an alternative to surgery to access the heart and blood vessels.
What are some reasons a patient would be sent to a cath lab by their care team?
Cath labs are an important part of treating heart conditions. A doctor may send a patient to a cath lab to diagnose and treat coronary artery disease, heart attacks, chest pain, congestive heart failure, peripheral (limb) vascular disease, pulmonary hypertension and even pulmonary embolisms, also known as blood clots.
Inside the cath lab, interventional cardiologists work with a team of nurses, procedural X-ray technicians and other support staff to quickly evaluate cardiovascular conditions and treat blockages and other problems in the arteries.
Common cath lab procedures include
- Cardiac coronary angiogram: This procedure evaluates the blood vessels supplying the heart using catheters and X-ray dye.
- Coronary stent placement: A procedure in which small metal scaffolds are placed within a blocked coronary artery to keep an artery open.
- Right heart catheterization: A procedure in which physicians examine blood flow and pressure filling in the right side of your heart
- Peripheral angiogram: A procedure that evaluates the flow of blood through arteries in the upper and lower extremities, similar to a coronary angiogram.
- Valve replacement: This minimally invasive procedure is done to implant an artificial valve in your heart to replace a narrowed heart valve.
Why do you need a cath lab?
Cath lab is a crucial component of treating heart issues. A catheterisation laboratory, sometimes known as a cath lab, is a procedural hospital room where tests and operations with a low risk of infection are carried out to identify and treat cardiovascular illness.
Catheters are small, flexible tubes used in procedures carried out in a cath lab, hence the name. These catheters might be used instead of surgery to reach the heart and blood vessels.
Diagnostics & Imaging for Cardiac Set-up
ECG, Echo, Ultrasound and Spirometer are the most common/basic diagnostic equipment available in all cardiac hospitals. Typical diagnostic equipment needed and related procedures that may be done in a cardiac facility are as follows:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) for 12-lead resting, ambulatory and Stress ECG
- Echocardiography (Cardiac ultrasound) for transthoracic echocardiography (2D, 3D and Doppler echo), Contrast echocardiography, Transesophageal echocardiography, Stress echocardiography etc.
- Ultrasound – investigations of the blood vessels in the neck, arms and legs
- Spirometry to help diagnose and monitor certain lung conditions by measuring how much air one can breathe out in one forced breath.
- Cardiac CT for non-invasive angiography or vascular imaging
- Cardiac MRI
- TMT (Treadmill Test/ Stress Test system)
Equipment for Cardiac CathLab

The most basic equipment required in a cardiac unit is the Cath Lab consisting of Angiography X-Ray system. All other advanced systems are used less frequently today in India and their usage depends on the case load and complexity being handled in the hospital.
- Cath Labs – A catheterization laboratory or cath lab is an examination room in a hospital or clinic with diagnostic imaging equipment used to visualize the arteries of the heart and the chambers of the heart and treat any stenosis or abnormality found. Cath Labs are commonly used for coronary angiography and angioplasty procedures. Popular makes and models in Cath Labs are Philips Allura Xper FD20/10, Philips Allura FC 9, FD 10, Siemens Artis family (Artis Pheno, Axiom Artis, Artis Z, Artis U), Toshiba Infinix 8000, GE Innova, Optima and Discovery family products.
- Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) for the sonographic visualization or OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) for Optical Visualization of coronary stenosis. Main IVUS makers are Boston Scientific, Volcano Therapeutics and Terumo. Abbots (St Jude Medical) OCT is popular.
- Intracoronary pressure measurements or Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) using pressure wires, which is used as an assessment of the severity of coronary stenosis. Cardiac CTs are also getting popular for FFR measurements in a non-invasive manner. Both GE and Siemens have Cardiac CTs.
- Ablation devices such as Excimer laser for the removal of scar tissue as part of device lead extraction procedures involving pacemakers and ICD devices or Rotablator for atherectory (An atherectomy is a procedure that utilizes a catheter with a sharp blade on the end to remove plaque from a blood vessel)
- Electrophysiology systems for the invasive diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias
- 3D mapping systems allowing precise visualization and 3D guidance during procedures to treat complex cardiac arrhythmias and pulmonary vein isolation
- Robotic navigation system used in the treatment of complex cardiac arrhythmias and pulmonary vein isolation
- Fibrillator
CVTS – Operating Room
- Cardiopulmonary bypass – Heart and lung machine or Mini extracorporeal circuit cardiopulmonary (MECC) bypass machine
- Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP)
- OT Table, OT Light, Anesthesia workstation and Cautery machine
Cardiac Intensive care Unit
- Ventilators
- Patient monitors
- Hemodynamic monitoring and management
- Dialysis
- Defibrillator