The ankle is made up of three bones:
the tibia (shin bone), which forms the inside, front, and back of the ankle
the fibula, which forms the outside of the ankle
the talus, a small bone that sits between the tibia and fibula and the heel bone
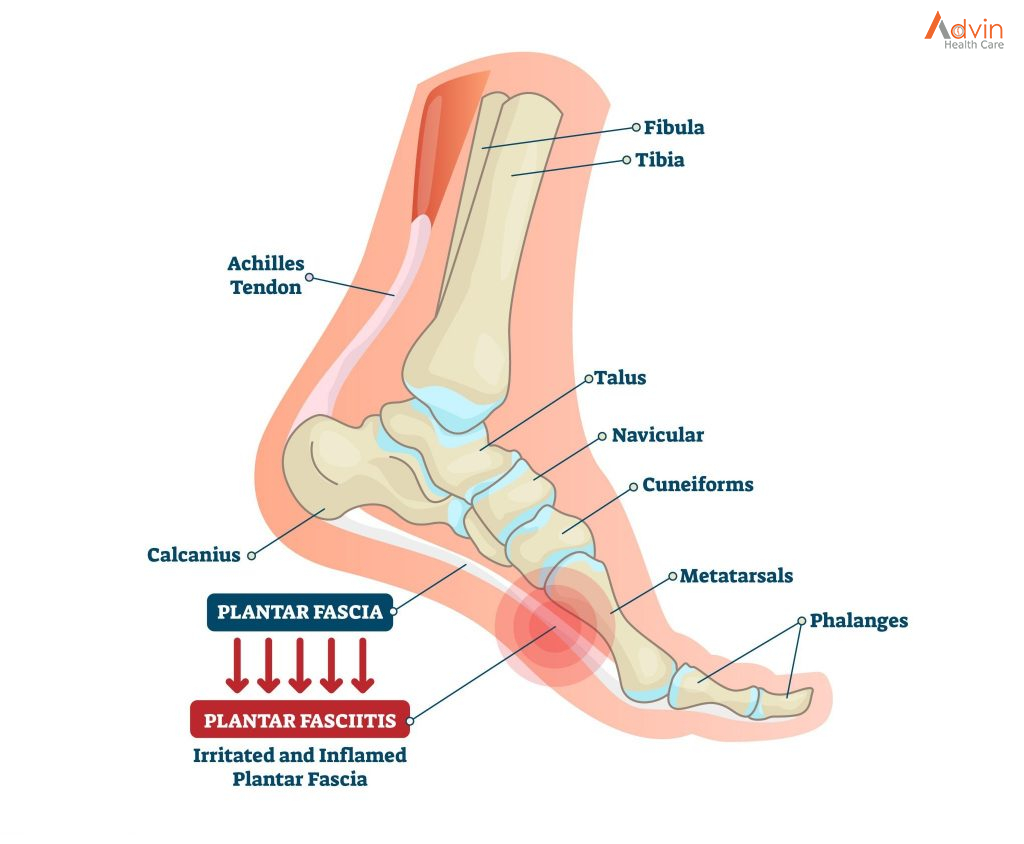
Parts of the ankle
The ends of these bones are called malleoli. The tibia has a medial (inside) malleoli and a posterior malleolus. The fibula forms the lateral (outside) malleoli.
A broken ankle (ankle fracture) occurs when the malleoli are broken. These fractures are very common. Ankle fractures happen with twisting of the ankle, falls, car accidents, or other injury. One, two, or all three malleoli can be broken. Ankle fractures can be displaced (out of place) or non-displaced. Symptoms of an ankle fracture include pain especially with weight bearing, swelling, bruising, and problems with ankle motion. X-rays help determine if treatment from a foot and ankle orthopaedic surgeon is needed.
The main goal of ankle fracture surgery is to put the ankle joint back in place and to stabilize the bones to heal. Getting the ankle joint back in place helps to decrease the risk of developing arthritis of the ankle. Stabilizing the ankle with plates and screws may allow earlier motion.
Ankle Fracture Symptoms
If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, it is very important that you get checked by your doctor to determine if you have a fracture:
- Throbbing pain
- Increased pain during activity and decreased pain during rest
- Bruising
- Inflammation, redness and tenderness
- A deformity of the bone in the foot and/or ankle
- Difficulty walking
- Difficulty bearing weight
How to Diagnose Ankle Fractures

To diagnose a foot and ankle fracture, you should be seen by an orthopaedic specialist to assess the severity of the injury and determine a plan for treatment. Imaging tests will likely be ordered, which may include:
- Musculoskeletal ultrasound
- MRI
- CT scans
- Weight-bearing CT scan
There are several types of fractures:
- Comminated fracture: the bone is broken into more than two pieces
- Extra-articular fracture: the break does not extend into the joint
- Intra-articular fracture: the break extends into the joint
- Open fracture: the fractured bone breaks the skin
Ankle Fracture Treatment Options
In some cases, if the fracture is mild and non-displaced (meaning the bone hasn’t shifted out of place), non-surgical treatment may be able to heal it. To treat foot fractures and ankle fractures without surgery, we typically follow the RICE protocol:
- Rest: Rest is key. Staying off your injury will help you heal faster. You will likely wear a cast to help keep the foot and ankle immobilized.
- Ice: Ice the area for 20 minutes at a time to help with swelling and inflammation. Continue icing every 40 minutes.
- Compression: Wrapping the injury helps control swelling.
- Elevation: Keep your foot and ankle raised slightly above the level of your heart to help reduce inflammation.
Are there different types of ankle fractures?
There are several types of ankle fractures affecting different parts of your ankle. Ankles are complicated. They’re made up of three bones and four ligaments, each doing a different job to keep your ankle in good working order. Here are the different types of ankle fractures:
- Lateral malleolus fractures: This injury can happen when you break the bony knob on the outside of your ankle. This is the most common type of ankle fracture.
- Medial malleolus fractures: This fracture happens when you break the bony knob on the inside of your ankle.
- Bimalleolar ankle fracture: This fracture happens when you break both bony knobs on your ankle. This is the second most common type of ankle fracture.
- Bimalleolar equivalent fracture: This fracture happens when you break both bony knobs on the outside of your ankle and you damage ligaments inside your ankle.
- Posterior malleolus fracture: There’s a bony section on the back of your tibia. This is your posterior malleolus.
- Trimalleolar fracture: In this case, all three parts of your ankle are broken.
- Pilon fracture: Your tibia ends in a section called the roof of your ankle. When you break this section, it’s called a Pilon fracture.
- Maisonneuve fracture: This fracture happens when you sprain your ankle and break the upper part of your fibula, near your knee.
- Syndesmotic injury: The syndesmosis joint is located between your fibula and tibia (shinbone) and anchored by ligaments. A syndesmotic injury happens when you have at least one fracture in your tibia or fibula and you sprain ligaments in your syndesmotic joint.
Ankle Fracture Surgery
If you have a more serious fracture, surgery is usually necessary to repair the fracture as well as any ligaments, tendons and muscles that have been damaged. Our orthopaedic surgeons are experts in fracture repair of the foot and ankle. We have the expertise to treat complex cases, including broken bones that haven’t healed properly (called non-union) and other types of traumatic fractures.
For complex wounds of the foot, we have a unique program called the Orthoplastic Limb Salvage Center, where a specialized team of orthopaedic surgeons and plastic surgeons work together to determine a plan for reconstructive surgery and operate together. Orthopaedic foot and ankle surgeons have expertise in treating all types of bone fractures and performing bone-grafting procedures, while plastic surgeons have specialized training and knowledge of soft tissue injuries that may accompany traumatic fractures.
The Penn Orthoplastic Limb Salvage Center is the only program of this kind in the U.S. that provides this level of integrated care and expertise in microsurgical and complex fracture treatment. All of the surgeons are accustomed to treating injuries that require multiple surgeries at the same time, including re-plantation of limbs and toes and specialized microvascular procedures to repair bones and soft tissues. We consistently combine highly advanced surgical specialties that ensure the best possible outcome for more serious fractures and wounds of the foot and ankle and prevent limb amputation for those at risk.
Some of the surgical treatments for foot and ankle fractures that we often perform are fixation surgery, non-union surgical repair and reduction surgery.
Ankle Fracture Fixation Surgery
If the fracture in your foot or ankle is displaced, or has caused misalignment of the bones, your orthopaedic surgeon will need to put the bones back into the correct position using specialized hardware such as plates, screws or pins. If necessary, we will perform bone grafting and may need to reconstruct soft tissues such as ligaments and tendons.
Non-Union Ankle Fracture Surgery
A non-union is a broken bone that did not heal properly. Treatment may entail surgery to remove an infection if present, to better stabilize the fracture, or to stimulate bone growth with a bone graft.
Our surgeons perform complex non-union surgical repair with vascularized bone grafting. Vascularized bone grafts allow living bone tissue to be transplanted to replace bone tissue that is damaged.
We are one of the few medical centres in the nation who perform vascularized bone grafting.
Ankle Reduction Surgery
If the fracture in your foot or ankle is displaced, or has caused misalignment of the bones, your orthopaedic surgeon will need to put the bones back into the correct position using specialized hardware such as plates, screws or pins. If necessary, we will perform bone grafting and may need to reconstruct soft tissues such as ligaments and tendons.
Advin Ankle Instrument Set
- Rochester-Pean Forceps
- Allis Tissue Forceps
- Crown Scissor
- Stevens Tenotomy Scissor
- TC Iris Scissors
- TC Metzenbaum-Lahey Dissecting Scissor
- TC Mayo-Stille Dissecting Scissor
- TC Metzenbaum Dissecting Scissor
- TC Wire Cutting Scissor
- Utility Scissor
- TC Halsey Needle Holder
- TC Crile-Murray Needle Holder
- TC Mayo Hegar Needle Holder
- Backhaus Towel Clamp
- Lorna-Edna Towel Clamp
- Foerster Sponge Forceps
- Adson Dressing Forcep
- Dressing Forceps
- Tissue Forceps
- Debakey Atraumatic Forceps
- Scalpel Handle
- Davis Brain Spatula
- Blair-Rollet Retractor 4 Prong
- Joseph Hook
- Ragnell Retractor
- Senn Retractor
- Miller-Senn Retractor
- US Army Retractor
- Volkman Retractor
- Weitlaner Retractor
- Deaver Scissor
- Holzheimer Retractor
- Mini Hohmann Bone Elevator
- Inge Retractor
- Cloward Vertebra Retractor
- Freer Elevator
- Key Elevator
- Sayre Elevator
- Adson Elevator
- Miller-Colburn Raspatory
- Double End Plain Serrations
- Maltz Raspatory Backward Cutting
- Bruns Bone Curette
- Lambotte Osteotome
- Hoke Osteotome
- Beyer Rongeur
- Boehler Bone Cutting Forceps
- Ruskin-Liston Bone Forceps
- TC Pin Cutter
- Flat Nose Plier with Side Cutter
- Probe With Eye
- Director and Tongue Tie
- Mallet With Two Plastic Ends



