Angioplasty
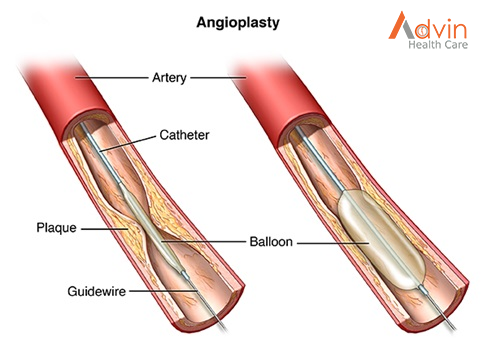
Angioplasty surgery is done to treat coronary artery disease and restore the blood flow in the body. In Angioplasty surgery, the doctors put a thin tube through the blood vessel containing a balloon at the end that helps push out the substances clotting the blood vessel.
Angioplasty can also be done in combination with stent placement. This combination helps reduce chest pain, breathing problems and reduce stroke risk.
Angioplasty is often combined with the placement of a small wire mesh tube called a stent. The stent helps prop the artery open, decreasing its chance of narrowing again. Most stents are coated with medication to help keep the artery open (drug-eluting stents). Rarely, bare-metal stents are used.
Angioplasty can improve symptoms of blocked arteries, such as chest pain and shortness of breath. Angioplasty is also often used during a heart attack to quickly open a blocked artery and reduce the amount of damage to the heart.
Why it’s done
Angioplasty is used to treat the build-up of fatty plaques in the heart’s blood vessels. This build-up is a type of heart disease known as atherosclerosis.
Angioplasty may be a treatment option for you if:
- You have tried medications or lifestyle changes but these have not improved your heart health.
- You have chest pain (angina) that is worsening.
- You have a heart attack. Angioplasty can quickly open a blocked artery, reducing damage to your heart.
Angioplasty isn’t for everyone. Depending on the extent of your heart disease and your overall health, your doctor may determine that coronary artery bypass surgery is a better option than angioplasty for you.
You may need coronary artery bypass surgery if:
- The main artery that brings blood to the left side of your heart is narrow
- Your heart muscle is weak
- You have diabetes and multiple severe blockages in your arteries
In coronary artery bypass surgery, the blocked part of your artery is bypassed using a healthy blood vessel from another part of your body.
How is Angioplasty Surgery performed?
The procedure to perform angioplasty might seem easy, but it is not that simple. While performing this surgery, doctors go through the following steps that are discussed below:
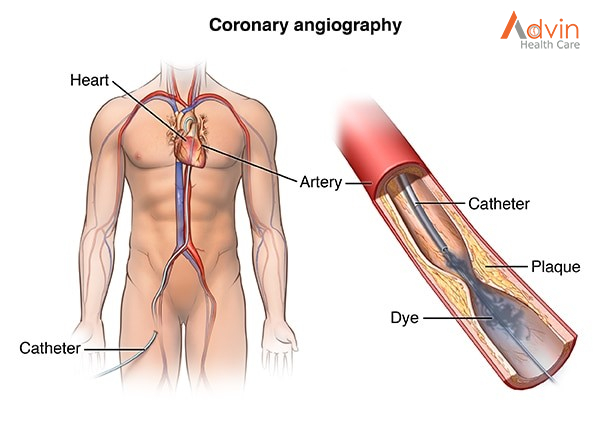
- The doctors insert a long, thin tube-like catheter in the crotch or wrist artery.
- The catheter is threaded into the affected artery using X-ray imaging.
- The surgeon then injects a liquid dye to check a blockage.
- Next, a catheter with a balloon is pushed through the first catheter and steered to the heart.
- The surgeon opens the balloon when the second catheter reaches its destination containing the blockage.
- After that, the balloon is removed along with the blockage.
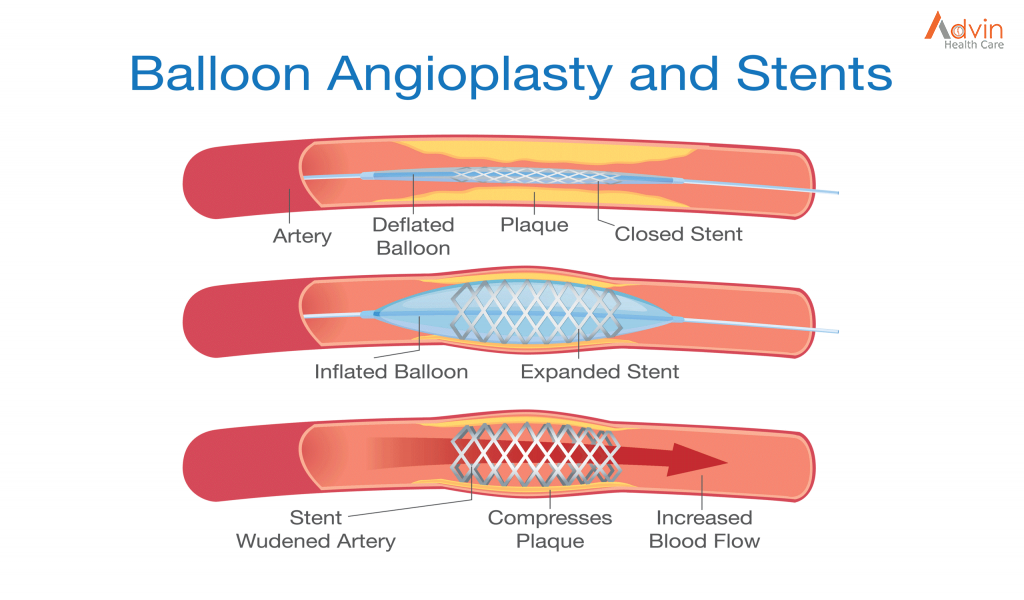
- If required, the surgeon will then push another thin tube called the stent.
- This stent placement prevents the blockage’s re-growth and the narrowing of the artery.
- In the last stage, the catheter is successfully removed.
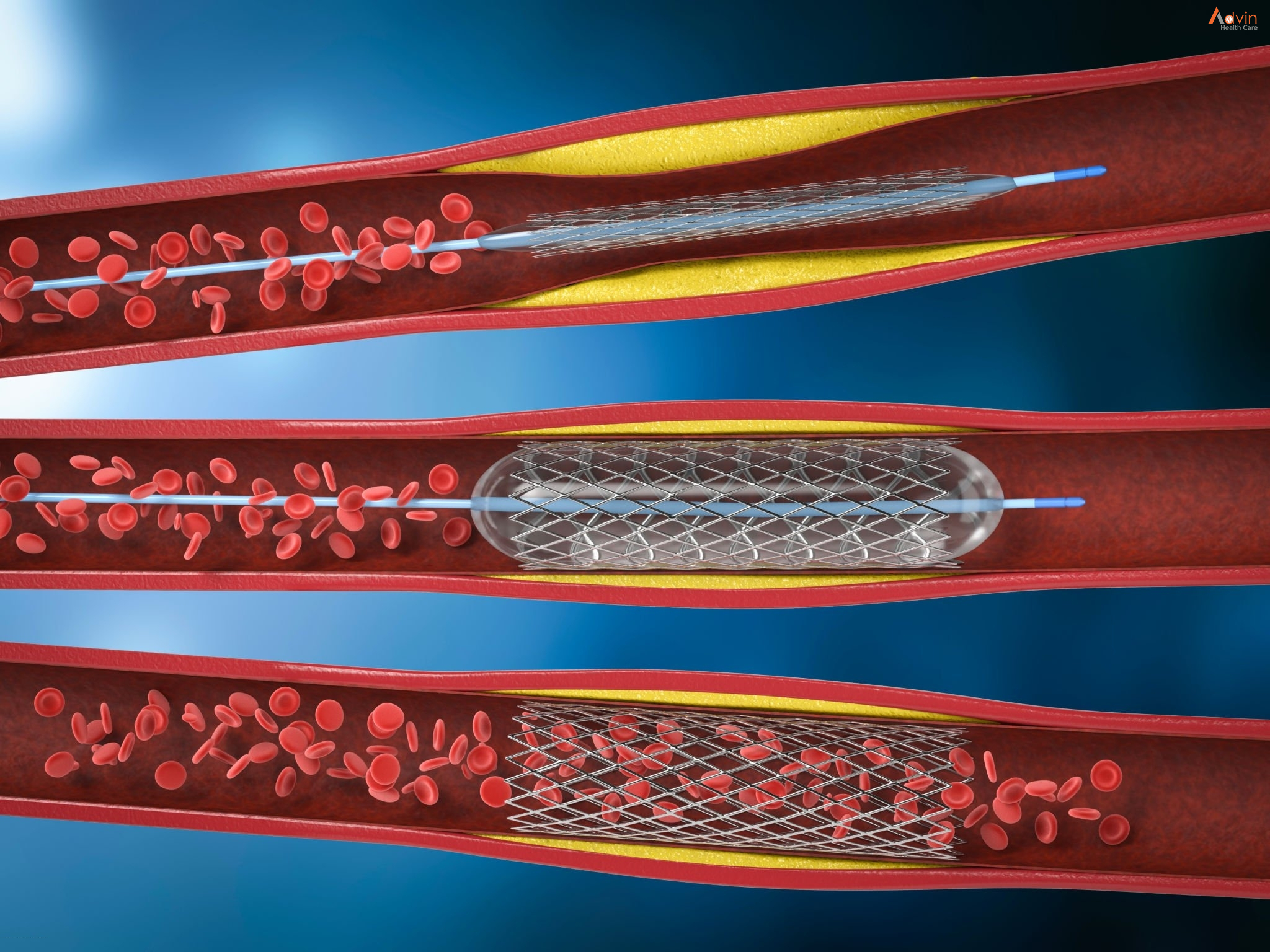
Stent placement
Most people who have angioplasty also have a stent placed in their blocked artery during the same procedure. A stent, which looks like a tiny coil of wire mesh, supports the walls of your artery and helps prevent it from re-narrowing after angioplasty.
Here’s what happens during a stent placement:
- The stent, which is collapsed around a balloon at the tip of the catheter, is guided through the artery to the blockage.
- At the blockage, the balloon is inflated and the spring-like stent expands and locks into place inside the artery.
- The stent stays in the artery permanently to hold it open and improve blood flow to your heart. In some cases, more than one stent may be needed to open a blockage.
- Once the stent is in place, the balloon catheter is deflated and removed.
- More X-ray images (angiograms) are taken to see how well blood flows through your newly widened artery.
Most stents implanted during an angioplasty are drug coated. The medication in the stent is slowly released to help prevent future plaque buildup and the re-narrowing of the blood vessel.
After your stent placement, your doctor will prescribe medications, such as aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix), ticagrelor (Brilinta) or prasugrel (Effient), to reduce the chance of blood clots forming on the stent.
Benefits of Angioplasty & Stenting
Treating blocked arteries with angioplasty and stenting:
- can save your life and reduce heart muscle damage during a heart attack by restoring blood flow to the heart
- may immediately relieve or at least reduce symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath and fatigue, making you feel better and able to do more each day
- can reduce the risk of stroke
- can improve functioning of the kidneys
- can restore blood flow to the legs to prevent gangrene and eliminate the need for amputation