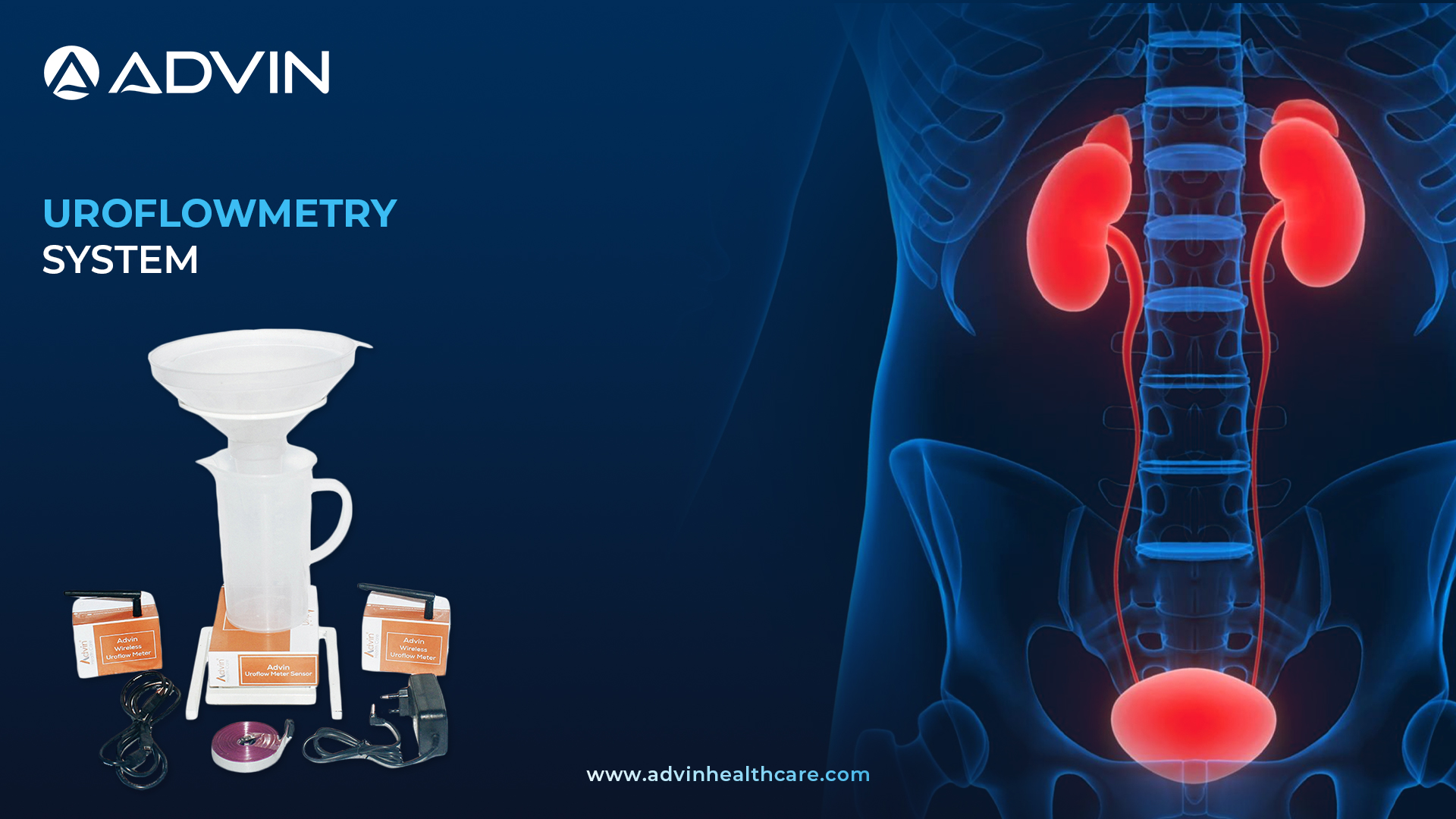
Introduction to Uroflowmetry System – Advanced Diagnostics for Urinary Flow Assessment
The Uroflowmetry System is a diagnostic medical device used to measure the flow rate of urine during voiding. It helps evaluate lower urinary tract function and detect abnormalities such as obstruction, weak bladder muscles, or other voiding disorders. It provides accurate, real-time analysis of urinary flow and voided volume.
Development & Evolution – Innovations in Non-Invasive Urological Testing Technology
Uroflowmetry was first introduced in the mid-20th century as a simple method to evaluate bladder outlet obstruction and voiding dysfunction. Early systems used mechanical devices to collect urine, but modern uroflowmetry systems are digital and computer-based, providing precise flow curves, maximum flow rate, average flow rate, and voiding time. Today, it is an essential tool in urology clinics worldwide.
Brief Overview – Role of Uroflowmetry System in Measuring Urine Flow Rate and Voiding Patterns
The Uroflowmetry System by Advin Health Care offers accurate and user-friendly uroflow testing. It records urine flow rate, flow pattern, and voided volume to assist in diagnosing conditions such as BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia), urethral strictures, overactive bladder, and neurogenic bladder. With a compact design and digital interface, it ensures efficient diagnosis in hospitals and clinics.
Clinical Applications – Diagnosis of Obstruction, Incontinence, Prostate Disorders, and Neurogenic Bladder
- BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) Evaluation
- Urethral Stricture Disease Diagnosis
- Overactive Bladder Assessment
- Neurogenic Bladder Disorder
- Pre and Post-Surgical Evaluation in Urology
- Pediatric Urology Functional Testing
How to Use – Step-by-Step Guidelines for Test Preparation, Measurement, and Data Interpretation
- Place the uroflowmeter in a private, comfortable space.
- Instruct the patient to void naturally into the uroflowmetry funnel.
- The system automatically measures urine flow and records the graph.
- Data is stored and analyzed by the software for interpretation.
- Clean and disinfect the device after each use.
Market Trends – Increasing Demand for Non-Invasive Urological Diagnostics Worldwide
The Uroflowmetry System is in high demand due to the increasing prevalence of urinary tract disorders and prostate diseases. With the rise in BPH cases among aging men, demand is growing in both developed and developing countries. Global trends show a shift toward portable, wireless, and software-integrated uroflow systems for easier clinical use and data sharing.
Also Known As – Urine Flow Analyzer, Uroflow Device, Non-Invasive Urology Diagnostic System
Uroflow meter, Urine Flow Measurement Device, Uroflowmetry Analyzer, Digital Uroflow System, Urinary Flow Test Machine
Advin Uroflowmetry System – Technical Specifications, Features, and Key Advantages
- Advin Health Care provides a highly advanced, compact, and reliable Uroflowmetry System designed for precise urological diagnosis. The system ensures accurate measurement, easy operation, and durable performance for hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers.
- Advin Uroflowmetry Systems are advanced, fully automatic devices designed to monitor urinary volume and flow rate. Both Wireless and PC-Based versions are weight-based, ensuring accurate measurements with graphical representation of urine flow. These systems provide non-invasive, reliable, and comfortable testing, suitable for day-to-day urodynamic studies.
Types Of Uroflowmetry System
- Wireless Uroflowmetry System
- PC Based Uroflowmetry System
Advanced Features – Both Systems
- Fully automatic with auto start and stop
- Weight-based flow sensors for precise measurements
- Graphical display of urine flow (Flow Rate vs Time, Volume vs Time)
- Data storage with patient information
- Non-invasive procedure – safe, comfortable, and cost-effective
- Lightweight, compact, and easy to operate
- International quality standard compliance
Get Connected:
+91-70717 27261 | urology@advinhealthcare.com | www.advinhealthcare.com